Newsletter: 172
Date: September 4, 2024
ECONOMIC SITUATION IN SPAIN
The Spanish economy in 2024 has shown remarkable resilience, but with nuances.
- Moderate growth: After a strong growth in 2023, Spanish GDP is expected to grow by around 1.8% in 2024, according to the latest forecasts from Funcas. This growth has been driven mainly by private consumption, which has held up well thanks to the improvement in the labour market.
- Inflation down: While inflation remains a concern, it has moderated from its highs. However, a high inflationary core persists, suggesting that the fight against inflation is not over yet.
- Labour market: The Spanish labour market continues to show signs of strength, with the unemployment rate continuing to fall. However, job quality and the pay gap remain major challenges.
- Tourism: The tourism sector, key to the Spanish economy, has registered a strong recovery after the pandemic, even exceeding pre-pandemic levels in some destinations.
- Uncertainty: The Spanish economy is facing a number of uncertainties, including the evolution of the war in Ukraine, tightening financial conditions, and the risk of a global recession.
Deindustrialisation in Spain is a recurring theme in economic debates. While it is true that the relative weight of industry in our GDP has decreased in recent decades, it is important to analyse the causes and consequences of this phenomenon, as well as the prospects for the future.
Causes of Deindustrialization in Spain
- Change in the production model: The transition from an economy based on heavy industry to a service economy, driven by globalisation and technological innovation, has been a key factor.
- Competitiveness: The difficulty of competing with low-labor cost countries, such as those in Asia, has led to the closure of many traditional industries.
- Automation: The increasing automation of production processes has reduced the demand for labor in the industrial sector.
- Offshoring: Many companies have moved their productions to countries with lower labor and regulatory costs.
Consequences of Deindustrialization
- Job loss: Deindustrialization has led to significant job losses in the manufacturing sector, especially in regions with strong industrial concentration.
- Increased dependence on imports: Declining industrial production has increased dependence on imports of manufactured goods.
- Lower value added: Services typically have lower value added per employee than industry, which can limit long-term economic growth.
- Territorial imbalance: Deindustrialisation has aggravated regional inequalities, concentrating economic activity in large cities and leaving behind rural and less developed areas.
Is there a negative trend for the primary and secondary sectors?
- Primary sector: The primary sector, especially agriculture, has experienced modernisation and a decrease in employment, although it is still important for the Spanish economy. However, it faces challenges such as climate change, international competition and land concentration.
- Secondary sector: The manufacturing industry has suffered a significant contraction, but there are sectors that are showing signs of growth, such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, and renewable energy.
Are we deindustrializing?
The answer is not simple and depends on how deindustrialization is defined. If it is understood as an absolute loss of industrial capacity, the answer would be no, since Spain is still an industrialized country. However, if we consider the relative loss of industry’s weight in GDP and employment, the answer would be yes.
It is important to note that deindustrialisation is not a phenomenon exclusive to Spain, but affects many developed countries.
Future prospects
- Reindustrialisation: There is a growing consensus on the need to promote the reindustrialisation of Spain, based on sectors with high added value, such as biotechnology, nanotechnology and the circular economy.
- Specialization: Spain should seek to specialize in sectors where it has competitive advantages, such as automotive, aeronautics, and renewable energy.
- Training: It is essential to invest in the training of workers to adapt them to the new professional profiles demanded by the industry of the future.
- Innovation: Innovation is key to increasing the competitiveness of Spanish industry and generating new jobs.
In conclusion, deindustrialization is a complex process with multiple causes and consequences. Although it is true that industry has lost weight in the Spanish economy, it is necessary to adopt measures to promote sustainable and knowledge-based reindustrialisation, which will create quality employment and improve the country’s competitiveness.
The Spanish economy has shown a certain capacity to adapt to global challenges, but uncertainty persists and it is necessary to continue closely monitoring the evolution of the international economy and national economic policies.
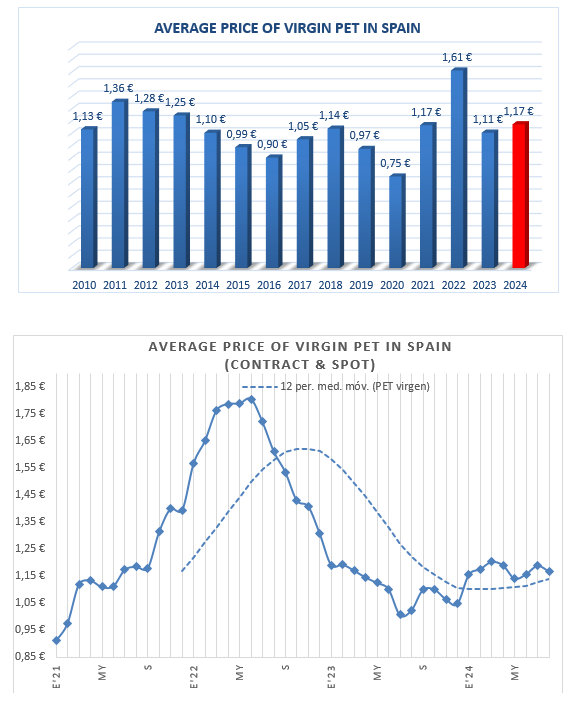
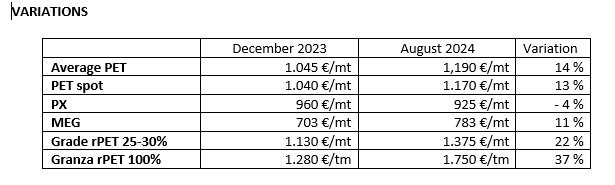
PET MARKET SITUATION
The Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) market in Europe is undergoing a significant transformation, marked by a series of announcements related to the shutdown and possible closure of production plants. This situation raises questions about the underlying causes and their implications for industry, consumers and the wider economy.
What’s happening?
Several interconnected factors are driving these changes in the PET market:
- Decreased Demand:
- Changing Consumption Habits: Growing environmental awareness and the search for more sustainable alternatives have led to a decrease in the consumption of PET-packaged products, especially in the beverage sector.
- COVID-19 pandemic: The pandemic accelerated certain trends, such as increased consumption at home and the use of returnable containers, which negatively impacted the demand for PET.
- Increased Production Costs:
- Commodity Price: PET is produced with petroleum-derived raw materials, so fluctuations in crude oil prices have a direct impact on production costs.
- Energy: High energy costs, especially of natural gas used in production processes, have also put pressure on companies’ margins.
- Environmental Regulations: The implementation of stricter regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and waste management has increased the operating costs of plants.
- Production Overcapacity:
- Oversupply: In recent years, new PET production plants were built in Europe and other regions, leading to overcapacity in the market.
- Competition: Intense competition among producers has led to lower prices and lower profit margins.
- Economic Uncertainty:
- War in Ukraine: The war in Ukraine has generated great uncertainty in energy markets and has affected supply chains globally.
- Inflation: Rising inflation has reduced consumers’ purchasing power and affected demand for non-essential goods.
Environmental and regulatory impact:
- European regulations: The Single-Use Plastics Directive and the Circular Economy are driving a transition towards more sustainable production and consumption models. This implies greater restrictions on the use of virgin PET and an incentive for recycling and reuse.
- Sustainable alternatives: Biodegradable, compostable and mechanically recycled materials are gaining ground as alternatives to PET, especially virgin PET. These materials offer similar properties but with a lower environmental impact.
- Recycling: Improving recycling technologies and creating markets for recycled PET are crucial to reducing reliance on virgin raw materials. However, the quality of recycled PET and plastic waste contamination remain major challenges.
Geopolitics and supply chains:
- War in Ukraine: The conflict has created uncertainty in energy markets and affected supply chains for key raw materials for PET production, such as oil and natural gas.
- Imports of recycled PET: Europe is heavily dependent on imports of recycled PET from countries such as China, Turkey, Indonesia, etc., which raises concerns about the quality of the material and the traceability of the waste.
- Supply chain resilience: Companies are looking to diversify their sources of supply and develop strategies to deal with market volatility and geopolitical risks.
Innovation and development of new products:
- New technologies: Nanotechnology, biotechnology and materials engineering are making it possible to develop new types of PET with improved properties, such as greater UV resistance and greater barrier to gases.
- New products and applications: PET is being used in a wide range of applications, from textile manufacturing to construction. In addition, new products with greater added value are being developed, such as smart packaging and PET-based bioplastics.
- Public-private collaboration: Collaboration between companies, research centres and governments is essential to promote innovation and the development of new solutions based on PET.
Implications for consumers:
- Changing consumption habits: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions and are looking for more sustainable and recyclable products.
- Lifecycle information: Transparency in product lifecycle information is key to enabling consumers to make informed decisions.
- Sustainability expectations: Consumers expect companies to take concrete steps to reduce their environmental footprint and offer more circular products.
Future prospects:
In the long term, the PET market is expected to continue to evolve towards a more sustainable and circular model. The growing demand for sustainable products, new regulations, and technological advancements will drive the adoption of more innovative and efficient solutions.
Implications
The consequences of this situation are multiple and can have a long-term impact on the PET market:
- Sector Consolidation: Consolidation of the sector is likely, with the acquisition of distressed plants by larger, more efficient companies.
- Plant Closures: The closure of production plants can lead to a decrease in supply and an increase in PET prices.
- Development of New Materials: The search for more sustainable alternatives to PET will drive the development of new packaging materials and technologies.
- Increased Recycling: An increase in PET recycling efforts is expected to reduce reliance on virgin raw materials.
In conclusion
The PET market in Europe is in a moment of transition, marked by a number of challenges and opportunities. Companies in the sector will have to adapt to this new environment, investing in more efficient and sustainable technologies, and looking for new business opportunities in an increasingly competitive market.
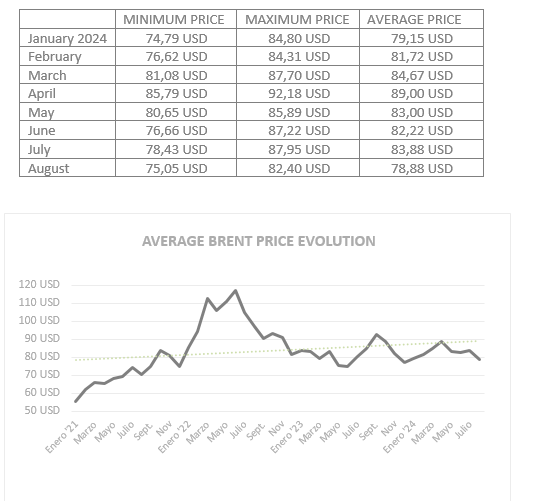
BRENT
The Brent oil market has exhibited moderate volatility during the first eight months of 2024, influenced by a combination of global and regional factors.
After a period of increased volatility in previous years, the price of Brent has shown a more stable trend, fluctuating within a relatively narrow range.
Despite the stability, prices have tended to exert downward pressure due to factors such as growing concerns about a potential global economic downturn, rising interest rates, and efforts by producing countries to stabilize the market.
OPEC+ decisions have played a crucial role in oil supply and therefore in determining prices. The production cuts agreed by the cartel have helped prop up prices.
The price of Brent has fluctuated between $75 and $92 per barrel during the first eight months of 2024.
Global oil demand has gradually recovered from pandemic lows, but growth has been slower than expected due to economic uncertainties and the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Year-end outlook:
Volatility is expected to continue to be a feature of the oil market due to global economic uncertainty, geopolitical tensions, and OPEC+ decisions.
Despite potential supply disruptions, downward pressure on prices is expected to persist due to rising supply and relatively weak demand.
In summary, the Brent oil market has shown relative stability in 2024, but uncertainty remains high. Investors should keep an eye on global economic developments, oil producers’ decisions, and trends in demand.
Sources: OPEC, IEA, Reuters
GDPR: Data Protection Information of MARSELLÀ GLOBAL S.L. (smarsella@marsellaglobal.com):
PURPOSE: To inform you of our products and services by electronic means. LEGITIMATION: Legitimate interest in keeping you informed in your capacity as a client and/or user. ASSIGNMENTS: Not contemplated. CONSERVATION: During the contractual relationship and/or until you request us to cancel the contract and during the periods required by law to meet any liabilities once the relationship has ended. RIGHTS: You can exercise your right of access, rectification, deletion, portability of your data and limitation or opposition in the email of the responsible party. In the event of disagreements, you can file a complaint with the 72Data Protection Agency (www.aepd.es).
This newsletter is prepared based on the information and experience of our sales team. Marsella Global, SL pays special attention to its preparation, however, we cannot guarantee the accuracy and usefulness of the content published.
The recipient accepts the content of this newsletter on the understanding that Marseille Global, SL is not responsible for any damage caused by the use of the information contained in this document.




Comments are closed.